Neuroradiology is a subspecialty of radiology that specializes in diagnostic imaging of the brain, spine and head & neck.
Neuroradiologists spend one or two years in fellowship training after diagnostic radiology residency focused on studying various diseases such as stroke, demyelinating disease, neurodegenerative disease, brain tumors, head and neck cancer, neurovascular disease, trauma, back pain and other neurologic diseases.
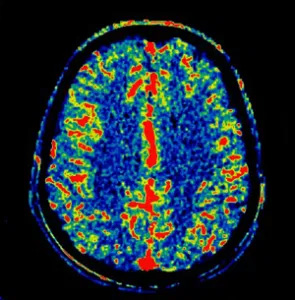
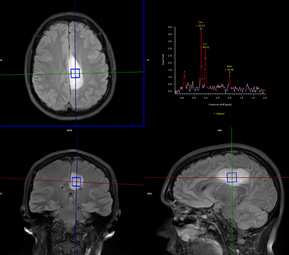
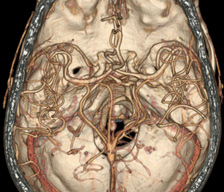
The primary imaging modalities are Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI); however MCR neuroradiologists also provide interpretations for more advanced imaging including functional MRI, spectroscopy, NeuroQuant, CT/MRI perfusion and parathyroid 4D CT. Neuroradiologists are also trained to perform procedures such as lumbar punctures and myelograms.
The MCR neuroradiologists work closely with both primary physicians and specialists, including neurologists, neurosurgeons and otolaryngologists. They participate weekly in the head & neck and neuro-oncology tumor board conferences, which are multidisciplinary conferences focused on complex cases.
Neuroradiology Procedures
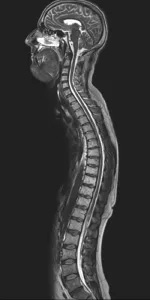
Lumbar Puncture
Lumbar puncture is a diagnostic procedure used to sample the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). Neuroradiologists use x-ray guidance to safely insert a small-caliber spinal needle through the skin at the lower back into the CSF. Using x-ray guidance typically results in a quicker procedure with less patient discomfort compared to non-image-guided lumbar puncture. This procedure is used to diagnose infections, tumors, and conditions such as multiple sclerosis affecting the brain and spinal cord.
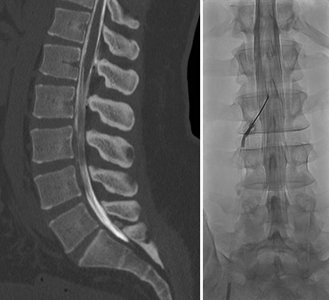
Myelography
Myelography is a diagnostic imaging procedure that provides images of the spinal cord and its nerves. This is a two-step procedure: first a lumbar puncture is performed, followed by injection of a contrast agent (dye) into the CSF through the spinal needle. Myelograms are typically followed by CT of the spine. The procedure is used to diagnose abnormalities such as a herniated disc, narrowing of the spinal canal, and tumors. It is used to supplement MRI or as an alternative if there are any contraindications to MRI.